Top 10 Uses of Tebuconazole Fungicide: Benefits and Application Guide
Tebuconazole fungicide has emerged as a leading solution in the agricultural sector, particularly in managing a wide array of plant diseases. As farmers seek effective ways to protect their crops, understanding the multifaceted uses of this fungicide becomes essential. Renowned agricultural expert Dr. Emily Harper states, "Tebuconazole fungicide has revolutionized disease management in agriculture, providing growers with a reliable tool to enhance crop health and yield." Her insights underline the importance of this chemical in maintaining robust agricultural practices.
The application of tebuconazole fungicide extends beyond mere disease control; it plays a pivotal role in improving agricultural efficiency and sustainability. Whether combating rusts, blights, or molds, the versatility of tebuconazole makes it an invaluable asset to modern farming methods. As we delve into the top ten uses of this fungicide, we will explore its benefits and application techniques, providing growers with a comprehensive guide to maximize its potential. Embracing such innovations is crucial for the future of agriculture, where effective disease management directly correlates with food security and sustainable farming practices.

Overview of Tebuconazole Fungicide and Its Mechanism of Action
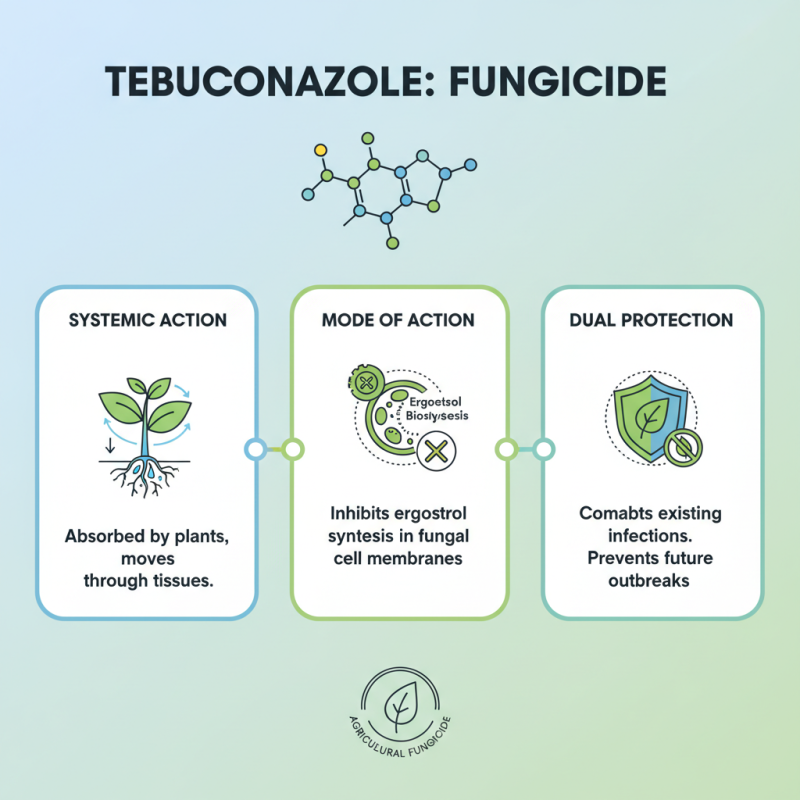
Tebuconazole is a systemic triazole fungicide widely used in agricultural practices to combat a variety of fungal diseases affecting crops. Its effectiveness lies in its unique mechanism of action, which primarily involves the inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis, a critical component of fungal cell membranes. By disrupting this process, tebuconazole compromises the integrity of the fungal cells, leading to their eventual death. This mode of action not only combats existing infections but also provides a preventive effect against future fungal outbreaks.
Moreover, tebuconazole exhibits a broad spectrum of activity, making it suitable for a range of crops, including cereals, fruits, and vegetables. Its systemic nature allows for effective absorption and translocation within the plant, offering protection both above and below ground. This characteristic enables tebuconazole to effectively manage diseases caused by a variety of pathogens such as rusts, mildews, and blights. Understanding the mechanism of action and application benefits of tebuconazole is crucial for optimizing its use in crop protection strategies, ensuring healthy yields and sustainable farming practices.
Key Agricultural Applications of Tebuconazole in Crop Protection
Tebuconazole is a widely used fungicide known for its effectiveness in crop protection. Its key agricultural applications include the control of various fungal diseases in crops such as wheat, barley, and soybeans. By inhibiting the ergosterol biosynthesis, Tebuconazole prevents the growth of pathogenic fungi, thereby protecting yields and enhancing crop quality.
Farmers use this fungicide during critical growth phases to mitigate the risk of diseases like powdery mildew and rust, ensuring healthier plants and more robust harvests.
Tips for Application: When applying Tebuconazole, timing is essential. It’s best to target early symptoms of disease to prevent serious outbreaks. Additionally, combining Tebuconazole with other integrated pest management strategies can enhance its effectiveness. Always adhere to recommended dosage guidelines and monitor weather conditions to optimize the treatment's efficacy.
Another notable use of Tebuconazole is in seed treatment, where it helps protect crops right from germination. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of soil-borne fungal infections, laying a strong foundation for plant growth. Implementing Tebuconazole in crop management plans not only safeguards crops but also contributes to sustainable agricultural practices by improving resource efficiency.
Tips for Seed Treatment: Ensure thorough coverage of seeds for optimal protection, and consider pre-treatment testing to identify potential fungal threats specific to your region. This targeted approach allows for more effective use of fungicides and better crop outcomes.
Benefits of Using Tebuconazole for Disease Management in Plants
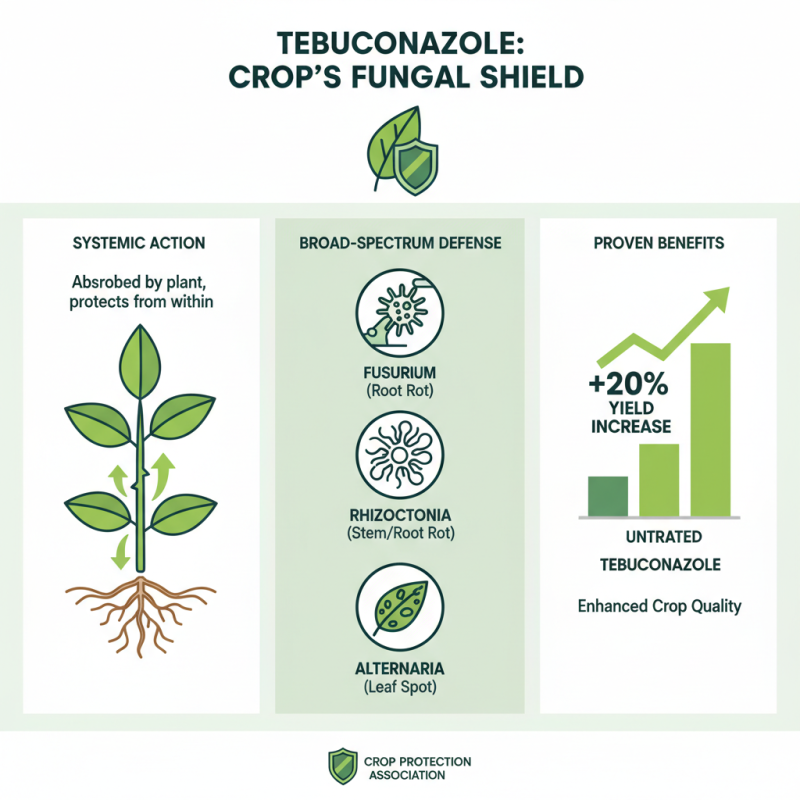
Tebuconazole is a systemic fungicide that has become increasingly popular among agricultural professionals for its effectiveness in managing a broad spectrum of fungal diseases in various crops. According to the Crop Protection Association, tebuconazole has proven effective against key pathogens such as Fusarium, Rhizoctonia, and Alternaria, which can severely impact crop yields and quality. Its ability to translocate within the plant enhances its protective capabilities, ensuring a prolonged defense against leaf spot diseases, root rot, and other fungal infections. In studies, its application has demonstrated yield increases of up to 20%, underscoring its significance in disease management strategies.
The preventative benefits of using tebuconazole extend beyond immediate disease control. Research conducted by the American Society of Agronomy indicates that timely applications can effectively shield plants during crucial growth stages, reducing the risk of infection incidents that could lead to total crop failure. Furthermore, implementing tebuconazole into integrated pest management programs not only helps in mitigating disease severity but also improves overall plant health, enhancing resistance to environmental stressors. This dual benefit contributes to more sustainable agricultural practices, making tebuconazole a valuable tool in modern crop production systems. The economic implications are significant, as growers can achieve higher marketable yields, ultimately enhancing profitability while promoting responsible fungicide use.
Best Practices for Tebuconazole Application in Field Conditions
When applying Tebuconazole fungicide in field conditions, it is crucial to follow best practices to ensure effectiveness while minimizing any potential negative impact on the environment. Before application, thoroughly assess the field for existing fungal diseases and weather conditions, as these factors can significantly influence the treatment's success. Timing is essential; applying the fungicide at the appropriate growth stage of the crop can enhance its efficacy. Additionally, monitoring environmental conditions such as humidity and temperature can help predict disease outbreaks and optimize application timing.
Proper application techniques further improve the performance of Tebuconazole. Use calibrated equipment to ensure accurate dosage and coverage, avoiding over-application that can lead to resistance or environmental harm. It's recommended to select the correct formulation based on field conditions and specific disease pressures. Furthermore, incorporating integrated pest management (IPM) strategies can provide a holistic approach, reducing reliance on fungicides while maintaining crop health. Rotating fungicides with different modes of action is also a key strategy to minimize resistance development in fungal populations.
Top 10 Uses of Tebuconazole Fungicide: Benefits and Application Guide
| Use Case | Target Disease | Crop Type | Application Rate (L/ha) | Optimal Timing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preventive Treatment | Septoria Leaf Spot | Wheat | 0.5-1.0 | Feekes 8-10 |
| Fungicide Resistance Management | Powdery Mildew | Barley | 0.75-1.5 | Early Flowering |
| Post-Harvest Treatment | Fusarium Head Blight | Corn | 1.0-2.0 | After Harvesting |
| Soil Drench | Rhizoctonia | Soybean | 0.5 | Planting Time |
| In-Furrow Application | Pythium | Potatoes | 0.6 | Before Irrigation |
| Field Spraying | Leaf Blight | Tomatoes | 0.4-1.0 | At First Signs of Disease |
| Seed Treatment | Seed Rot | Various Crops | 0.3 | Before Sowing |
| Mixing with Other Products | Various Diseases | Field Crops | 0.5 | Depending on Companion Products |
| Foliar Application | Leaf Spot Diseases | Fruits and Vegetables | 0.4-1.0 | During Active Growth |
Environmental Considerations and Safety Measures for Tebuconazole Use
The application of Tebuconazole as a fungicide is prevalent in agricultural practices due to its efficacy against a range of fungal pathogens. However, with its widespread use comes significant environmental considerations that must be addressed to mitigate potential ecological impacts. According to a report by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Tebuconazole's persistence in soil and potential for groundwater contamination are critical factors to consider. Studies indicate that Tebuconazole can remain detectable in the environment for several months, necessitating careful management practices to prevent runoff into water bodies.
To ensure safe application, it is essential to implement proper safety measures. This includes adhering to recommended dosage guidelines and timing, which are crucial to reducing the risk of drift and non-target exposure. The National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS) emphasizes the importance of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, which consist of monitoring field conditions and applying fungicides only when necessary. Moreover, protective equipment should be worn during application to minimize risks to human health, considering that inhalation or skin contact can lead to adverse effects. Understanding these environmental and safety considerations will support responsible use of Tebuconazole, fostering sustainability within agricultural systems while managing fungal diseases effectively.
Related Posts
-

Top Strategies for Effective Crop Protection in Modern Agriculture
-

Top 10 Corn Fungicides: Boost Your Yield with Effective Disease Control
-

How to Effectively Use Thiamethoxam Insecticide in Your Garden
-
How to Choose the Best Fungicides for Crop Protection in 2025
-

2025 Top Digital Innovations in Agriculture Featuring Corteva Herbicide Solutions
-

How to Improve Crop Science Techniques for Sustainable Agriculture Solutions

