Effective Strategies for Pesticide Control in Organic Farming Practices
In the realm of organic farming, the challenge of pesticide control remains a critical focus as the demand for organic produce continues to rise globally. According to the USDA Organic Report, organic food sales reached approximately $62 billion in 2021, highlighting the growing consumer preference for products perceived as healthier and more environmentally friendly. However, despite these advantages, organic farmers face significant challenges in managing pests effectively while adhering to organic standards.
Renowned expert Dr. Emily Thompson, a leading figure in sustainable agriculture, emphasizes the importance of innovative pest management strategies in her recent study: “Effective pesticide control is not only vital for the health of organic crops but also essential for maintaining the integrity of the organic farming system.” As farmers strive to balance pest control with organic principles, understanding the selection and application of approved pest management techniques is imperative for sustainable farming practices.
To navigate the complexities of pesticide control, organic farmers are increasingly turning to integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, ecological pest control methods, and the use of organic-approved pesticides. This approach not only mitigates pest pressure but also enhances biodiversity and soil health, providing a comprehensive solution that aligns with the foundational goals of organic agriculture. As the organic farming sector evolves, embracing effective pesticide control strategies will be paramount in ensuring long-term sustainability and productivity.

Overview of Pesticide Control in Organic Farming

Pesticide control in organic farming is fundamental to maintaining the integrity of organic produce while ensuring ecological balance. The approach to pesticides in organic farms is inherently different from conventional methods, emphasizing natural alternatives and management strategies that minimize harm to the environment and human health. Organic farming practices prioritize the use of natural pesticides, which are generally derived from plant or mineral sources, and which aim to control pests and diseases without the synthetic chemicals associated with conventional agriculture.
In effective pest management, strategies such as crop rotation, intercropping, and the introduction of beneficial insects are commonly utilized to prevent pest outbreaks. These practices promote a healthy ecosystem that naturally regulates pest populations. Regular monitoring of crops allows farmers to identify potential pest problems early, enabling timely intervention using organic-approved treatments that can include neem oil, insecticidal soaps, or biological control agents. Furthermore, education and training for farmers on integrated pest management (IPM) techniques are crucial, as they equip them with the knowledge to apply sustainable strategies tailored to their specific farming conditions. By combining these natural practices, organic farming can successfully manage pests while fostering biodiversity and protecting soil health.
Importance of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies play a crucial role in organic farming, providing a holistic approach to pest control that minimizes reliance on synthetic chemicals. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), IPM combines various practices to manage pest populations at acceptable levels, ensuring both crop health and environmental sustainability. By integrating cultural practices, biological controls, and agroecological techniques, farmers can enhance resilience against pest invasions while promoting biodiversity.
Research indicates that adopting IPM can lead to significant reductions in pest infestation and crop losses. A study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Ethics highlighted that farms implementing IPM strategies reported a 20% decrease in crop damage due to pests, alongside an increase in beneficial insect populations. Moreover, the USDA’s National Organic Program recognizes that IPM not only helps in managing pests effectively but also supports organic certification requirements, fostering a more sustainable agricultural model.
The emphasis on monitoring, forecasting pest outbreaks, and implementing preventative measures helps in creating a balanced ecosystem, which is vital for the long-term success of organic farming.
Natural Pesticides and Their Role in Organic Farming
Natural pesticides play a vital role in organic farming, offering an environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic chemicals. Unlike conventional pesticides, natural options derive from plant, animal, or mineral sources and are designed to minimize harm to non-target organisms, including beneficial insects and the surrounding ecosystem. For instance, neem oil and diatomaceous earth are commonly utilized to manage pests while preserving the health of the soil and biodiversity on the farm. These products often target specific pests without disrupting the overall balance of the agricultural environment, making them suitable for organic practices.
Moreover, the use of natural pesticides aligns with the holistic philosophy of organic farming, which emphasizes sustainability and ecological health. Farmers can integrate these pesticides into integrated pest management (IPM) systems by applying them at the right time and under the right conditions to optimize their effectiveness. Additionally, adopting practices such as crop rotation and the encouragement of beneficial insects can help to reduce pest populations and the need for intervention. By leveraging natural pesticides along with other sustainable methods, organic farmers can cultivate healthy crops while fostering a resilient agricultural ecosystem.
Cultural Practices to Minimize Pest Infestation
Cultural practices play a pivotal role in minimizing pest infestation in organic farming. By creating an ecosystem that promotes biodiversity, farmers can naturally manage pest populations. One effective approach is the practice of crop rotation, which disrupts the life cycles of pests that thrive on specific crops. By alternating the types of crops grown in a particular area, farmers can reduce the likelihood of pest establishment and infestation, as many pests are host-specific.
Additionally, incorporating companion planting can significantly deter pests while enhancing crop productivity. Certain plants, when grown together, can repel detrimental insects or attract beneficial predators. For example, planting marigolds alongside vegetables can deter nematodes and certain beetles, while legumes can enhance soil fertility, indirectly supporting plant health and making crops less susceptible to pest damage. Moreover, maintaining healthy soil through composting and natural amendments can promote strong plant growth, further reducing vulnerabilities to pest attacks. These cultural practices not only mitigate pest pressures but also align with the principles of sustainable and organic farming, fostering a more resilient agricultural ecosystem.
Monitoring and Evaluation Techniques for Pest Control Effectiveness
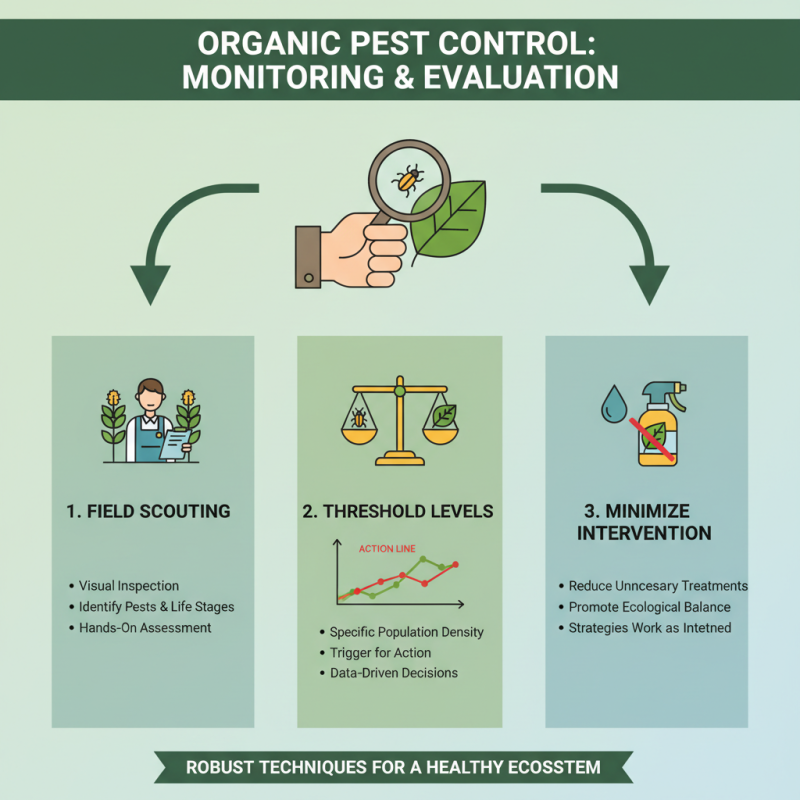
Effective pest control in organic farming relies heavily on robust monitoring and evaluation techniques to ensure that strategies are working as intended. One fundamental approach is regular field scouting, where farmers can visually inspect crops for signs of pest activity. This hands-on assessment allows for immediate identification of pests and their life stages, which can inform decisions about intervention methods. Using threshold levels—specific pest population densities that trigger action—farmers can make data-driven choices, minimizing unnecessary treatments and promoting ecological balance.
In addition to visual inspections, farmers can employ traps and lures to monitor pest populations more quantitatively. These tools help in capturing data over time, offering insights into pest behavior and population dynamics. Evaluation techniques, such as comparing crop yields before and after implementing control measures, further provide critical feedback on the effectiveness of pest management strategies. By analyzing this data, farmers can refine their approaches, adapt to changing pest pressures, and ultimately enhance both crop health and sustainability in their organic farming practices.
Related Posts
-

7 Essential Tips for Effective Pesticide Control: Boost Crop Yields by 30%
-

2025 Top Digital Innovations in Agriculture Featuring Corteva Herbicide Solutions
-

10 Best Corteva Chemicals for Sustainable Agriculture: Enhancing Crop Yields by 20%
-

Top 10 Cypermethrin Insecticide Uses for Effective Pest Control Solutions
-

10 Best Agriculture Chemical Solutions for Sustainable Farming in 2023
-

Top 10 Corteva Chemicals for Sustainable Agriculture Practices

