How to Effectively Use Thiamethoxam Insecticide in Your Garden
Thiamethoxam insecticide has emerged as a powerful tool for gardeners seeking to safeguard their plants from a variety of pests. Renowned entomologist Dr. Emily Harper, an expert in integrated pest management, emphasizes the significance of proper application techniques, stating, "Using thiamethoxam insecticide can be highly effective if deployed with precision and care." This statement underscores the necessity for gardeners to understand not only the benefits but also the best practices for using this advanced insecticide.
In today's dynamic gardening landscape, where pest resistance poses a significant challenge, thiamethoxam insecticide offers a reliable solution. As systemic insecticides, they work by being absorbed into the plant, providing protection from the inside out. However, to maximize its effectiveness while ensuring environmental safety, it is crucial for gardeners to learn the right methods and timings for application. As we delve deeper into the strategies for effectively utilizing thiamethoxam insecticide in your garden, we will explore tips, considerations, and best practices that will empower gardeners to cultivate thriving, pest-resistant plants.

Understanding Thiamethoxam: Composition and Function in Insect Control
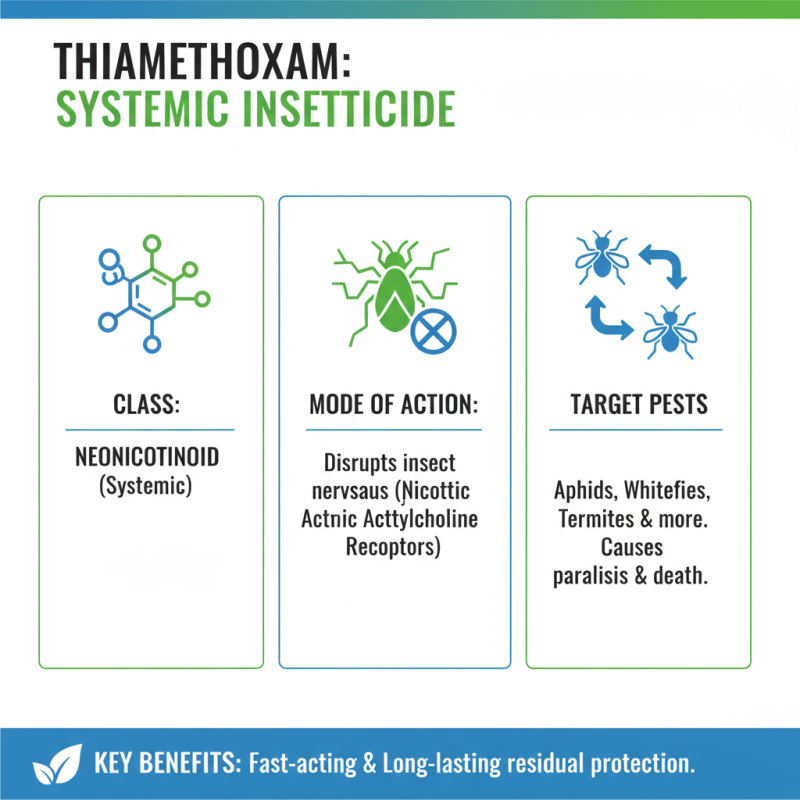
Thiamethoxam is a systemic insecticide belonging to the neonicotinoid class, known for its effectiveness in controlling a wide range of pests. This compound operates by disrupting normal nervous system functions in insects, specifically targeting nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. When pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and termites come into contact with or ingest thiamethoxam, it can lead to paralysis and ultimately death. Its mode of action not only provides swift results but also allows for residual effectiveness, which can offer prolonged protection against infestations.
In addition to its immediate impact on pest populations, thiamethoxam’s systemic properties mean that it can be absorbed by plants, offering a layer of protection over an extended period. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in garden settings, as it enables plants to defend themselves against pests that feed on their sap or foliage. However, understanding the correct application methods and dosages is crucial to maximize its efficacy while minimizing potential harm to beneficial insects and the surrounding ecosystem. Proper timing and adherence to recommended guidelines can create a balanced approach to insect management, ensuring healthy growth for garden plants.
Benefits of Using Thiamethoxam in Your Garden Pest Management Strategy
Thiamethoxam is a neonicotinoid insecticide that has gained attention for its efficacy in managing various pest populations in gardens. One of the primary benefits of using Thiamethoxam is its targeted action against harmful pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and corn rootworms, which can significantly damage crops and ornamental plants. According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), neonicotinoids like Thiamethoxam can reduce pest populations by up to 75% when applied correctly, providing gardeners with a strong line of defense while promoting healthier plant growth.
Another significant advantage of Thiamethoxam is its unique mode of action, which translates into longer-lasting pest control compared to many traditional insecticides. Research from the American Society of Agronomy indicates that Thiamethoxam can remain effective in the soil for several weeks, reducing the need for frequent applications and allowing beneficial insects such as pollinators to thrive in the garden environment. This residual effectiveness not only aids in minimizing pest outbreaks but also contributes to a more sustainable pest management strategy by reducing the overall chemical load in the ecosystem.
Effectiveness of Thiamethoxam Insecticide in Pest Management
This chart illustrates the effectiveness of Thiamethoxam insecticide against various garden pests. The data indicates high effectiveness percentages across different pest types, enhancing the pest management strategy in your garden.
Application Methods: How to Properly Use Thiamethoxam Insecticide
When using Thiamethoxam insecticide in your garden, proper application methods are essential to maximize its effectiveness while minimizing potential harm to beneficial insects and the environment. One effective approach is to apply it as a foliar spray. To do this, dilute the insecticide according to the manufacturer’s guidance, typically mixing it with water in a spray bottle or garden sprayer. Ensure you cover both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves, as insects often hide in these areas. Timing is crucial; applying the spray during the early morning or late afternoon can reduce the risk of evaporation and exposure to beneficial insects.
Another recommended method for applying Thiamethoxam is through soil drenching or incorporation into the soil. This approach is particularly effective for targeting pests that reside beneath the soil. To use this method, mix the insecticide with water and apply it directly to the soil around the base of the plants. It is important to follow the dosage instructions carefully to avoid harming the plants. Incorporating Thiamethoxam in this way ensures that it is absorbed by the root system, providing systemic protection against pests that may attack the plant. Always remember to wear protective gear during application to safeguard yourself from any potential exposure.
Safety Precautions and Environmental Considerations When Using Thiamethoxam
When using thiamethoxam insecticide in your garden, it's crucial to prioritize safety precautions and consider its environmental impact. Thiamethoxam, a neonicotinoid insecticide, is effective against a variety of pests, but it has been linked to adverse effects on non-target organisms, especially pollinators like bees. Studies indicate that thiamethoxam can linger in the environment, persisting in soil and water, leading to potential toxicity to non-target species. According to a report from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, the presence of neonicotinoids in waterways raises concerns regarding aquatic ecosystems. Thus, it's essential to apply thiamethoxam judiciously to mitigate its risks.
Tips for safe usage include applying thiamethoxam during calm weather to minimize drift and ensuring that nearby flowering plants are protected or covered. Additionally, always wear protective gear, including gloves and masks, when handling the insecticide to avoid skin contact or inhalation of the chemical. It is also advisable to follow the recommended dosage on the product label, as over-application not only increases environmental risks but can also lead to reduced efficacy against targeted pests.
Moreover, consider integrating thiamethoxam into an integrated pest management strategy, using it as a last resort. By employing alternative pest control methods, such as biological controls or organic insecticides, you can decrease dependency on synthetic chemicals while still managing pest populations effectively. Engaging in practices like crop rotation and companion planting can further enhance garden health, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
How to Effectively Use Thiamethoxam Insecticide in Your Garden - Safety Precautions and Environmental Considerations
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Target Pests | Aphids, Thrips, Whiteflies |
| Application Rate | 0.5 to 1.5 fl oz per 1,000 sq ft |
| Application Timing | Early morning or late afternoon |
| Safety Precautions | Wear gloves, goggles, and a mask during application |
| Environmental Considerations | Avoid application near water sources to prevent contamination |
| Re-entry Interval | 24 hours |
| Mode of Action | Neonicotinoid - affects the nervous system of insects |
| Resistance Management | Rotate with insecticides of different modes of action |
Monitoring and Managing Pests After Thiamethoxam Application in Gardens
After applying thiamethoxam insecticide in your garden, it is crucial to monitor and manage the pest situation effectively. One of the first steps is to observe the treated areas closely for any signs of pest activity. Look for visible damage on leaves, stems, and fruits to gauge the effectiveness of the treatment. Regularly inspecting your plants will help determine if additional applications of thiamethoxam are necessary or if alternative pest control methods should be considered.
In addition to monitoring, it is essential to manage environmental conditions that can influence pest populations. Maintain healthy garden practices such as proper watering, fertilization, and pruning, as these can strengthen plant resistance to pests. Integrated pest management techniques, like introducing beneficial insects or using organic deterrents, can also play a significant role in keeping pest populations at bay. By combining vigilant monitoring with holistic garden management, you can enhance the effectiveness of thiamethoxam and ensure a thriving garden ecosystem.
Related Posts
-

10 Best Corteva Chemicals for Sustainable Agriculture: Enhancing Crop Yields by 20%
-

Top 5 Benefits of Using 2 4 D Herbicide for Effective Weed Control in Agriculture
-

Top 10 Corn Fungicides: Boost Your Yield with Effective Disease Control
-

7 Essential Tips for Effective Pesticide Control: Boost Crop Yields by 30%
-

2025 Top 5 Innovations in Chemical Control for Sustainable Solutions
-

What Are the Best Pesticides for Plants: A Complete Guide for Gardeners

