10 Best Practices for Using Pesticides in Agriculture?
Effective use of pesticides in agriculture is vital for crop protection and food security. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), global pesticide use reached 5.2 million tons in 2019. This substantial figure highlights the dependence on chemicals to manage pests and diseases. However, the challenges of sustainable use persist, and best practices are crucial.
Dr. Emily Johnson, an expert in agricultural sciences, emphasizes, "The need for responsible pesticide use cannot be overstated." Farmers must balance pest control and environmental health. Many practices can enhance safety and efficacy but require caution. For instance, relying solely on chemical solutions may harm beneficial insects and soil health.
Improving pesticide efficacy often means rethinking application methods and schedules. The goal is to protect crops while minimizing negative impacts. A detailed understanding of local ecosystems and pest populations can guide appropriate usage. Strategies like integrated pest management (IPM) combine biology with chemical control, ensuring a more sustainable approach. However, the journey is fraught with complexities and often requires ongoing reflection and adaptation.
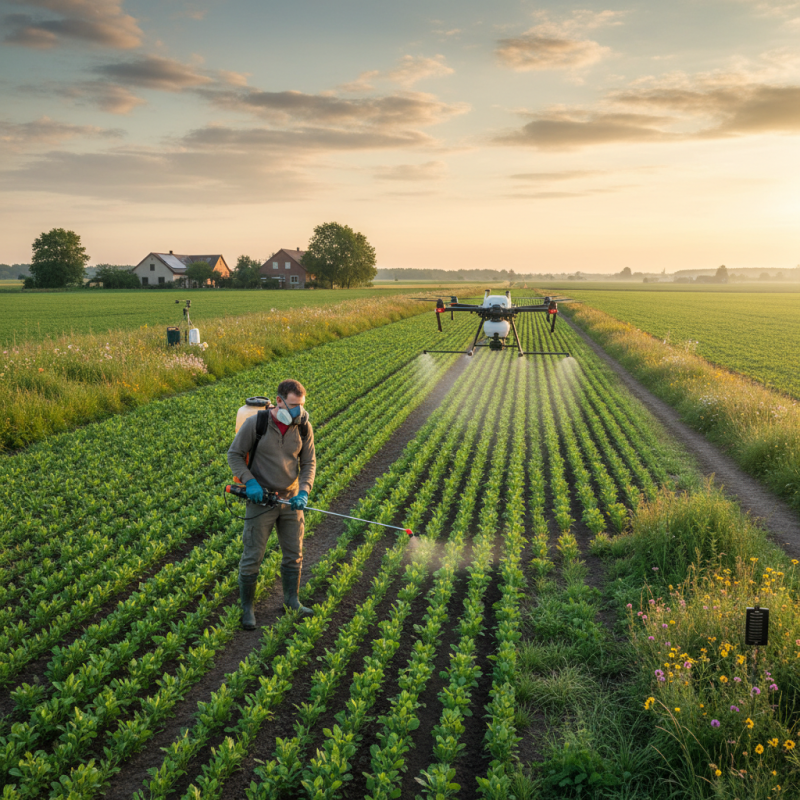

Best Practices for Pesticide Application Timing to Maximize Efficacy
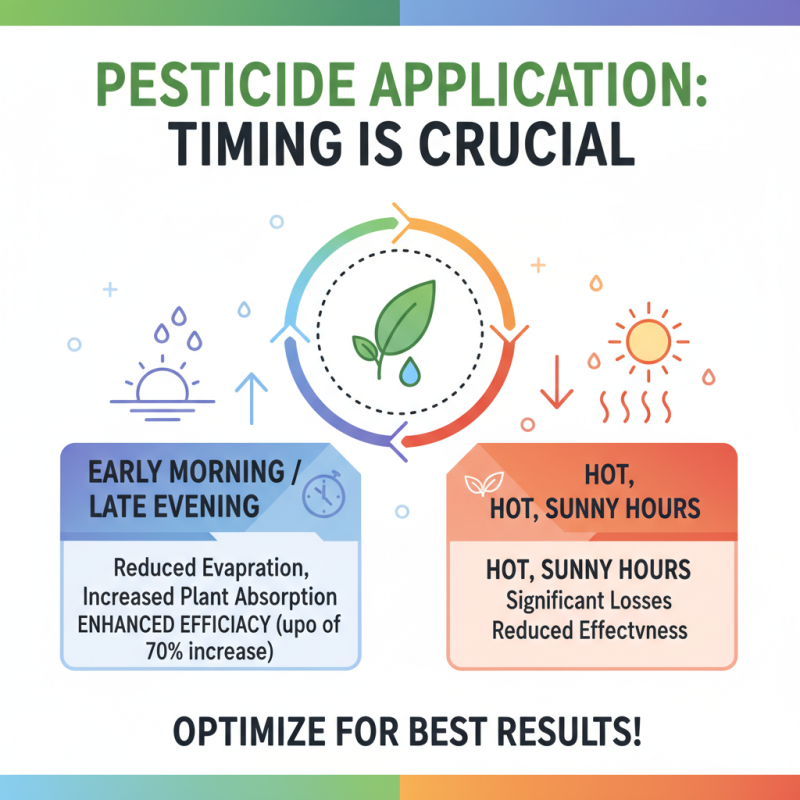
Timing is crucial for effective pesticide application. Studies show that up to 70% of pesticide efficacy depends on the timing of application. For instance, applying pesticides during the early morning or late evening can reduce evaporation and increase the absorption by plants. This enhances the overall effectiveness of the product. In contrast, applications made during hot, sunny hours can lead to significant losses.
Furthermore, understanding pest life cycles assists in determining the optimal timing for treatment. For example, applying pesticides when pests are most vulnerable can drastically improve control rates. Research indicates that targeting the early growth stages of pests can result in a 30% reduction in population. However, relying solely on timing without considering environmental factors often leads to disappointment.
Weather conditions play a significant role too. Rain can wash away pesticide residues, reducing their effectiveness. Ideally, a 24-hour window of dry conditions post-application is recommended. Yet, some farmers experience challenges in adhering to this due to unpredictable weather. This inconsistency highlights a common struggle in agricultural practices. Improving awareness and gathering precise weather data can help farmers make better application decisions.
Understanding Pesticide Label Instructions for Safe and Effective Use
Understanding pesticide label instructions is crucial for farmers. Each pesticide label contains essential information about usage, precautions, and application rates. Missing these details can lead to ineffective treatments or, worse, damage to crops. Many farmers often overlook the importance of checking expiration dates or storage conditions listed on the label. This oversight can diminish the pesticide's effectiveness.
It's essential to pay attention to safety precautions mentioned on the label. Protective gear is often recommended, yet some ignore this advice. Exposure to pesticides can have serious health consequences. Additionally, mixing different chemicals without guidance can create harmful reactions. Remembering to follow the recommended mixing ratios can save time and money in the long run.
The label also provides guidance on environmental considerations. For example, it may advise against application before rain. Many farmers wish to act quickly, but impatience can lead to runoff and soil contamination. Acknowledging these labels and reflecting on past mistakes can lead to wiser pesticide use. By taking the time to truly understand these important details, better decisions can be made for both crop health and safety.
Impact of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) on Pesticide Use Reduction
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) focuses on sustainable practices to reduce pesticide use. It emphasizes various strategies, including biological control, crop rotation, and habitat manipulation. A report from the Food and Agriculture Organization states that IPM can reduce pesticide use by 30% to 50% in many cropping systems.
Farmers adopting IPM often see improved biodiversity and soil health. A study revealed that farms practicing IPM had 15% higher yields while reducing chemical inputs. However, implementing IPM requires knowledge and training. Not all farmers are equipped to make the shift. There can be a steep learning curve, leading to doubts about its effectiveness.
Over-reliance on chemical solutions still exists in many regions. This creates resistance in pest populations, complicating the IPM approach. Farmers need ongoing education and support to overcome these challenges. The transition to IPM is not without obstacles, but the potential benefits are substantial. Balancing traditional methods and innovative practices is essential for sustainable agriculture.
Evaluating Environmental Factors in Pesticide Application Strategies
In agriculture, the thoughtful application of pesticides is crucial. Environmental factors play a significant role in determining the effectiveness and safety of these chemicals. For instance, studies indicate that temperature and humidity greatly influence pesticide evaporation and degradation. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), pesticides can degrade faster under high temperatures, which may reduce their effectiveness.
Soil type also affects pesticide performance. Sandy soils tend to allow quicker leaching, while clay soils can retain pesticides longer. This variance can lead to unintended contamination of groundwater. A report from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) highlighted that improper application strategies could lead to significant crop yield losses, sometimes exceeding 30%. Poor strategies not only harm the environment but also affect farmers' livelihoods.
Lastly, timing is crucial. Applying pesticides during unfavorable weather conditions can enhance drift and unintended off-target effects. The National Agricultural Statistics Service notes that many farmers struggle with weather patterns, highlighting the need for improved forecasting tools. Without these tools, farmers might find themselves applying pesticides in less-than-ideal conditions, leading to further environmental risks. Reflecting on these factors can help improve pesticide application strategies.
10 Best Practices for Using Pesticides in Agriculture
This bar chart illustrates the importance level of various best practices for using pesticides in agriculture, rated on a scale from 1 to 10. It highlights the significance of proper timing, targeted application, and safety precautions among other factors in effective pesticide use.
Importance of Post-Application Monitoring for Pesticide Effectiveness and Safety
Post-application monitoring is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness and safety of pesticide use. After application, farmers must observe the treated areas for signs of pesticide impact. This includes checking for pests, plant health, and any adverse effects on beneficial organisms. Monitoring helps ensure that pesticides work as intended. It also allows farmers to make timely adjustments if necessary.
Farmers often overlook this step. They may assume that once the pesticide is applied, the job is done. However, this is not the case. If pests persist or new issues arise, it may signal that the pesticide application was inadequate. Additionally, monitoring for potential runoff into water sources is essential. This vigilance prevents contamination and protects surrounding ecosystems.
Effective post-application monitoring requires a dedicated approach. Keeping detailed records of observations is important. This data can inform future applications and guide pest management strategies. Engaging with local agricultural extensions can provide valuable insights. Inconsistencies in results may highlight the need for better practices or different pesticide choices.
Related Posts
-

What Are the Best Pesticides for Plants: A Complete Guide for Gardeners
-

How to Improve Crop Science Techniques for Sustainable Agriculture Solutions
-
Effective Strategies for Pesticide Control in Organic Farming Practices
-

Why Are Agricultural Chemicals Essential for Modern Farming?
-

Top 10 Corteva Chemicals for Sustainable Agriculture Practices
-

2025 Top 5 Innovations in Chemical Control for Sustainable Solutions

